skin cancer screening
- Dr Owais Rafiq
- August 12, 2024
- 6:21 am
Skin cancer Screening and Protection
It is the outcome of the random growth of epidermal cells. Skin cells are the first to grow into cancer, which causes abnormal development or alterations. Most of skin disease cases are brought about by delayed sun openness or different factors. Some types of skin cancer are more likely to spread to other parts of the body. That is why, skin cancer screening and protection is very crucial. Clinical specialists can utilize the cells to decide the type of skin disease growth.
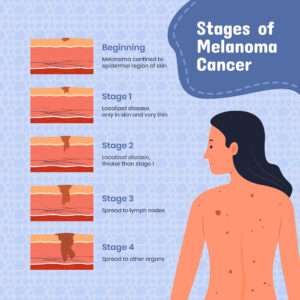
Types
The best method to understand the situation is to first understand the different types of skin cancer and how they affect the body.
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Melanoma
- Merkel cell carcinoma
Causes and risks of skin cancer
UV radiation from the sun and UV tanning bed use are the main causes of skin cancer. This could include prolonged exposure or short periods of intense sunburn.
- Age
The risk of getting skin cancers other than melanoma increases with age. On the other hand, kids might also develop skin cancer.
- Sun exposure
In the sun, sun exposure is the primary cause of the majority of skin cancerous growths. UV rays from daylight damage skin cells’ DNA. This harm could start years before cancer manifests itself.
- Previous skin cancer
Individuals who have previously received a skin cancer diagnosis are at a higher risk of developing the disease again than those who have not.
- Family history of skin cancer
If one of your family members already has squamous cell skin disease (SCC), your chances of developing it increase.
- Compromised immune system
You may be more susceptible to skin cancer in the future if your immune system is weakened by inflammatory conditions.
- Chemicals
Working with specific chemicals like petroleum products and coal tar and in certain occupations can raise your risk of developing skin cancer.
Skin cancer symptoms
Skin cancers can present with a wide range of symptoms and appearances. A few of the symptoms match those of other illnesses.
Typical signs of skin cancer include a region of skin that is:
- appears abnormal
- aches, itchy, bleeds, crusts, or scabs for more than four weeks
- doesn’t cure in four weeks.
- A wound that doesn’t heal
- The sore may appear transparent, glossy, pink, or brilliant white. It may appear red as well. It could have sharp edges, hurt, or feel sore.
Ulcer
Keep an eye out for a skin rupture (ulcer) that does not heal after four weeks and for which you cannot come up with an explanation.
A lump
This could be little, shiny, pink or red, and grow slowly.
Your skin has red spots.
It’s possible that these red areas are itchy. Other non-cancerous skin disorders could be the cause of this. But just to be sure, have it checked.
Moles or freckles
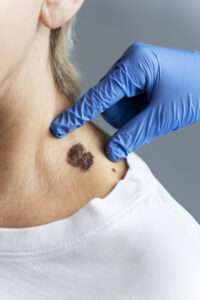
A shift in a mole or freckle may indicate melanoma, a different kind of skin cancer.
Skin cancer screening A comprehensive skin cancer screening is essential for early detection and treatment. By conducting regular screenings, healthcare professionals can identify any suspicious moles or lesions that may indicate skin cancer. Early intervention significantly increases the chances of successful treatment and improved outcomes. Therefore, it is crucial to prioritize routine skin cancer screenings to maintain optimal skin health.
Skin cancer screening is a crucial procedure for early detection and prevention of skin cancer. It involves thorough examination of the skin to identify any suspicious lesions or abnormalities. Regular screenings are recommended, particularly for individuals with a history of sun exposure or other risk factors. Early detection through skin cancer screening can significantly improve treatment outcomes and increase the chances of successful recovery.
The most popular method for skin cancer screening is looking for side effects. A skin cancer screening shows symptoms of the illness on every part of your skin. Early detection of skin cancer through skin cancer screening can lead to more positive treatment options. You can consult a doctor for skin screening, or you can examine your skin yourself to look for any symptoms. Tests may be necessary to determine whether a strange spot on the skin is cancerous.

A skin cancer screening is important if you:
- Notice a suspicious area of skin during a self-test
- Have had skin cancer before. In this instance, it is usually advisable to schedule a normal yearly skin disease screening with your supplier or a dermatologist.
- Are more susceptible to developing skin cancer.
To conduct a self-test to detect skin illness, you will examine your skin for:
- Changes in size, structure, or color of a mole or spot
- Oozing, fading, rough, or dried up skin patches
- Painful moles
- Sores that haven’t recovered in around fourteen days
- Shiny pink or red regions
Tests for skin cancer screening
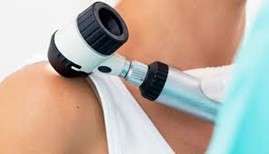
The main test for skin cancer screening involves taking a sample of the area.
It’s not simple to differentiate between skin cancer and non-cancerous skin. A doctor applies some oil on your skin and use a device called dermatoscope to examine the affected area closely.
Biopsy
A doctor takes a sample of skin to check if you have skin cancer. Using local anesthetic Your affected area is first numbed, depending on the size of the abnormal area and its location. They send the sample to the laboratory for microscopic examination.
Types of biopsies
Different types of biopsies take place, including:
Incisional biopsy: A little portion of the affected area is removed by the doctor with a surgical knife. The skin is removed from its entire thickness.
Excisional biopsy: The entire abnormal region is removed with this biopsy. The layer of healthy tissue that protects the afflicted area is also eliminated.
Punch biopsy: A doctor uses a special instrument to take a punch biopsy. They remove only a small portion of the abnormal area of the skin.
Shave biopsy: Your doctor uses an instrument to slice off the upper layer of skin or lesion.
Results of the biopsy
The results of your biopsy take two to three weeks to arrive.
If there are any cancerous cells in the skin sample, you must treat the affected area. For example, total removal of that region, or further treatments like topical creams.
Other tests
If you are diagnosed to have skin disease development, your physician will take a look at the lymph nodes surrounding the sickness. Biopsies or extra testing, for example, X-ray or CT scan, will be performed on any lymph nodes that seem to be enlarged or swollen. These tests can likewise help with showing how cancerous growth affects neighboring structures, like nerves.
Risk of screening: There are no risks directly associated with skin cancer screenings, but anxiety may increase as a result. If someone notices a suspicious spot but has to wait for an appointment to receive a skin biopsy for an accurate diagnosis, they may become nervous.
Skin cancer Protection and prevention
- Attempt to avoid the sun as much as you can, particularly between the long periods of 10 a.m. furthermore, 3 p.m.
- On uncovered skin areas, utilize a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a SPF of no less than thirty that blocks UVA and UVB beams.
- Sunscreen should be reapplied frequently, ideally every two hours, particularly after swimming or heavy sweating.
- Skip tanning booths and UV beds. Pick products that will adhere to your skin better and repulse water.
- Apply a lip balm with a minimum of 15 SPF.
- When you go outside, wear a helmet and other sun protection. Better protection is offered by tightly woven, darker-colored fabrics.
- Put on UV-blocking shades.
- Get a professional skin checkup from a dermatologist once a year at the latest.
- Regularly check your skin from head to toe.
| screening,biopsies,skinypink,basalcell |
Dr Owais Rafiq
Subscribe to Dr Owais YouTube channel
For parenting advice, child health, symptoms, causes and treatment of illness in children.