Leg length discrepancy – what is it?
- Dr Owais Rafiq
- August 15, 2024
- 1:33 pm
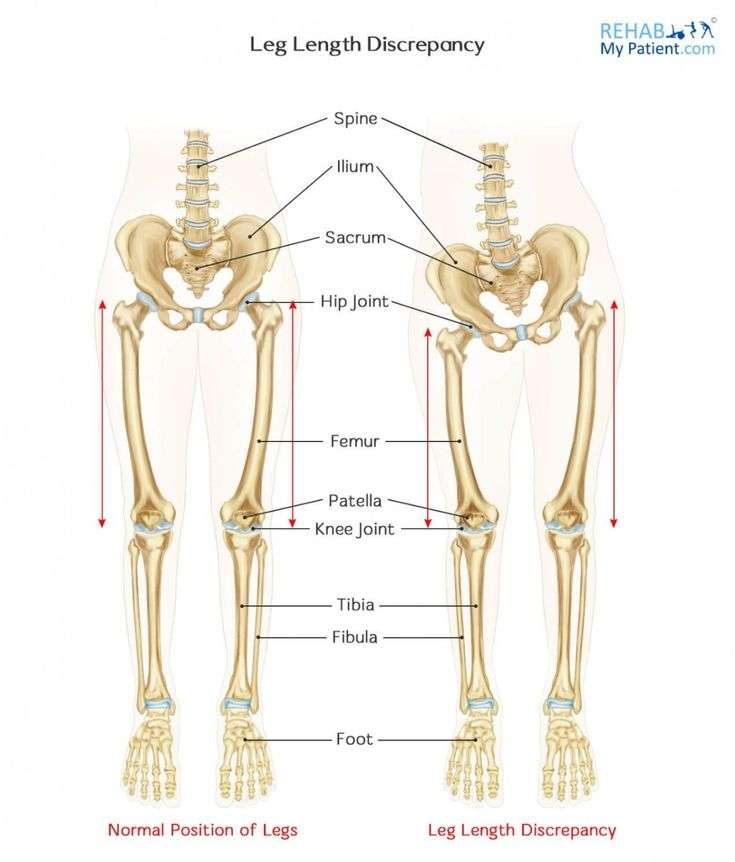
This is a condition where the leg on one side is shortened. Many children have different lengths of their legs which change from a little to a bigger one, with one leg being shorter than the other.
What determines Leg Length Discrepancy?
The Leg length discrepancy is a complicated issue with a number of reasons and almost 1/3 of world’s population has a length difference that does not affect their function at all and sometimes to the degree of missing a limb segment.
Causes such as
dysplasia of hip, clubfoot, hemimelia, etc.
Paralytic disorders such as cerebral palsy and spina bifida fall in this category of diseases
It may also occur as secondary to trauma, infection, or tumor.
In the vast majority of cases, shortening of one leg causes a leg length discrepancy while unusual elongation of one leg is present exclusively in syndromic or vascular conditions.

How does leg length discrepancy impact my child??
The difference between both legs is usually above 1. Moreover, prolonged issues may cause several complications in the long term including spinal, hip and knee issues.
- Abnormal growth, hip arthritis and scoliosis: when the child stands in an upright position the unequal length of the legs causes the pelvis to tilt to the shorter side causing an increase of pressure over the hip joint of the shorter limb, with time this increases pressure may manifest as hip pain and the child may be noticed to have a limp, this tilting of the pelvis over a period of time may also lead to curving of the back bone of the child, a condition called scoliosis.
- Gait abnormality: A leg length discrepancy of > 1 cm results in gait asymmetry.
- Back pain
What are the special tests for leg length discrepancy??
In clinical settings, leg length discrepancy is initially screened by keeping blocks under the child’s leg till the pelvis is levelled, a measuring tape is sometimes used to measure the length of the 2 limbs.
Special radiographs called scannogram that includes the profile of the whole limb from hips to the ankle joint are done to measure the difference accurately
How much LLD is normal in children??
In general, if the leg length discrepancy is less than 1.5 cm it does not cause any functional disability and no treatment is required.
How LLD is treated??
In children with a leg length discrepancy of 1.5-4 cm conservative measures such as shoe lifts may be utilized in the form of insoles, heel wedges or sole lifts.
LLD of greater than 5 cm requires surgical equalization, there are multiple options ranging from shortening of the longer side via temporary or permanent growth arrest through the growth plate.
Limb lengthening of the shorter side in case of secondary causes of LLD where there was temporary damage to the growth plate of the child following trauma or infection, the part of the growth plate may be excised allowing the bone to regrow over time.
In cases of un reconstruct able difference in the limb, amputation and prosthetic fitting may be considered
Can the child outgrow LLD??
In cases where the cause of LLD is due to damage of growth plate excision of damaged portion may provide an opportunity for leg to outgrow to the normal length, on the contrary in patients’ wit congenital LLD, the affected leg us continuously growing slower than normal leg.
Dr Owais Rafiq
Subscribe to Dr Owais YouTube channel
For parenting advice, child health, symptoms, causes and treatment of illness in children.