Insect Bites (Skin O Trauma & Injuries Kids’ Health)
- Dr Owais Rafiq
- September 28, 2023
- 8:52 pm
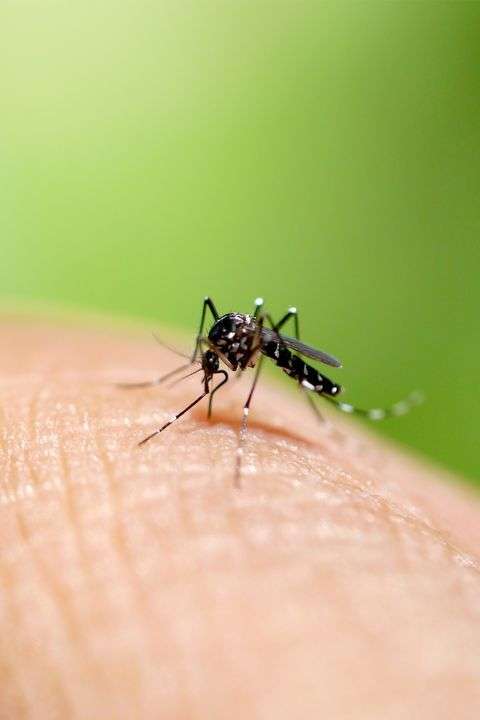

As parents, it’s important to be knowledgeable about common insect bites and stings that our children may encounter. While most of these incidents are not serious, knowing how to identify, treat, and prevent them can provide peace of mind.
Understanding Insect Bites and Stings
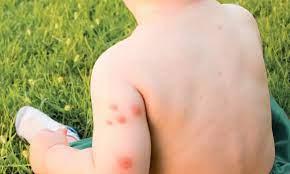
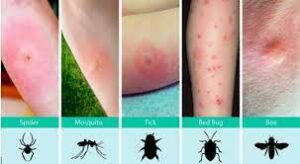
Insect bites and stings are typically caused by
- Mosquitoes
- Fleas
- Spiders and fire ants
- Ticks
- Wasps
- Bees and hornets
- Beetles.
The risk of insect-borne diseases is generally low, especially in urban areas. However, allergic reactions can occur in response to these bites, and in rare cases, a severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis can occur. The size and severity of the reaction may vary depending on the child’s sensitivity and degree of allergy.
Signs and Symptoms
When your child is bitten or stung by an insect, they may experience a range of symptoms. These can include:
- A minor skin reaction with a painful and itchy lesion at the site
- A more significant reaction with swelling, redness, and even blisters
In severe cases, anaphylaxis (severe life-threatening reaction) may occur, characterized by
- A widespread rash
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling of the lips or tongue
- Fainting
It’s essential to recognize these signs and take appropriate action.
Home Care for Insect Bites and Stings
In most cases, insect bites and stings can be treated at home. Follow these steps:
- Wash the affected area.
- Use plain, unscented moisturizing cream to alleviate itchiness.
- Apply cool, wet towels or face washers to reduce pain and swelling.
- If the bite or sting is on an arm or leg, encourage your child to rest with the limb raised above the heart level.
- Over-the-counter antihistamine creams or lotions can provide relief from itching.

When to Seek Medical Attention
While many insect bites and stings can be managed at home, there are situations where medical attention is necessary. Take your child to the doctor if:
- They experience severe pain that does not subside.
- The swelling or itching worsens after 24-48 hours.
- The child has difficulty breathing.
- A child gets unconscious after insect bites.
- If your child has had a severe allergic reaction in the past
Your doctor may prescribe oral steroid medication or an adrenaline autoinjector (e.g., EpiPen) for future incidents.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing insect bites and stings is key to ensuring your child’s well-being.
Follow these strategies:
- Cover exposed skin with long-sleeved shirts and pants.
- Keep picnic food covered and clean up spills immediately.
- Stay away from stagnant water areas, which are breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
- Avoid perfumes and scented products that may attract insects.
- Install insect screens on windows to keep bugs out.
- Use insect repellents according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Consider applying repellents to clothing rather than directly on the skin for young children.
Wrap up
By understanding the nature of insect bites and stings, recognizing their symptoms, and implementing preventive measures, parents can confidently navigate these common occurrences. Remember, most incidents can be managed at home with proper care, but seeking medical attention when needed is crucial to ensure the well-being of your child. Stay informed, and prepared, and enjoy the outdoors with peace of mind.
Dr Owais Rafiq
Subscribe to Dr Owais YouTube channel
For parenting advice, child health, symptoms, causes and treatment of illness in children.