Cardiovascular Exercises for Adults
- Dr Owais Rafiq
- September 28, 2023
- 8:53 pm
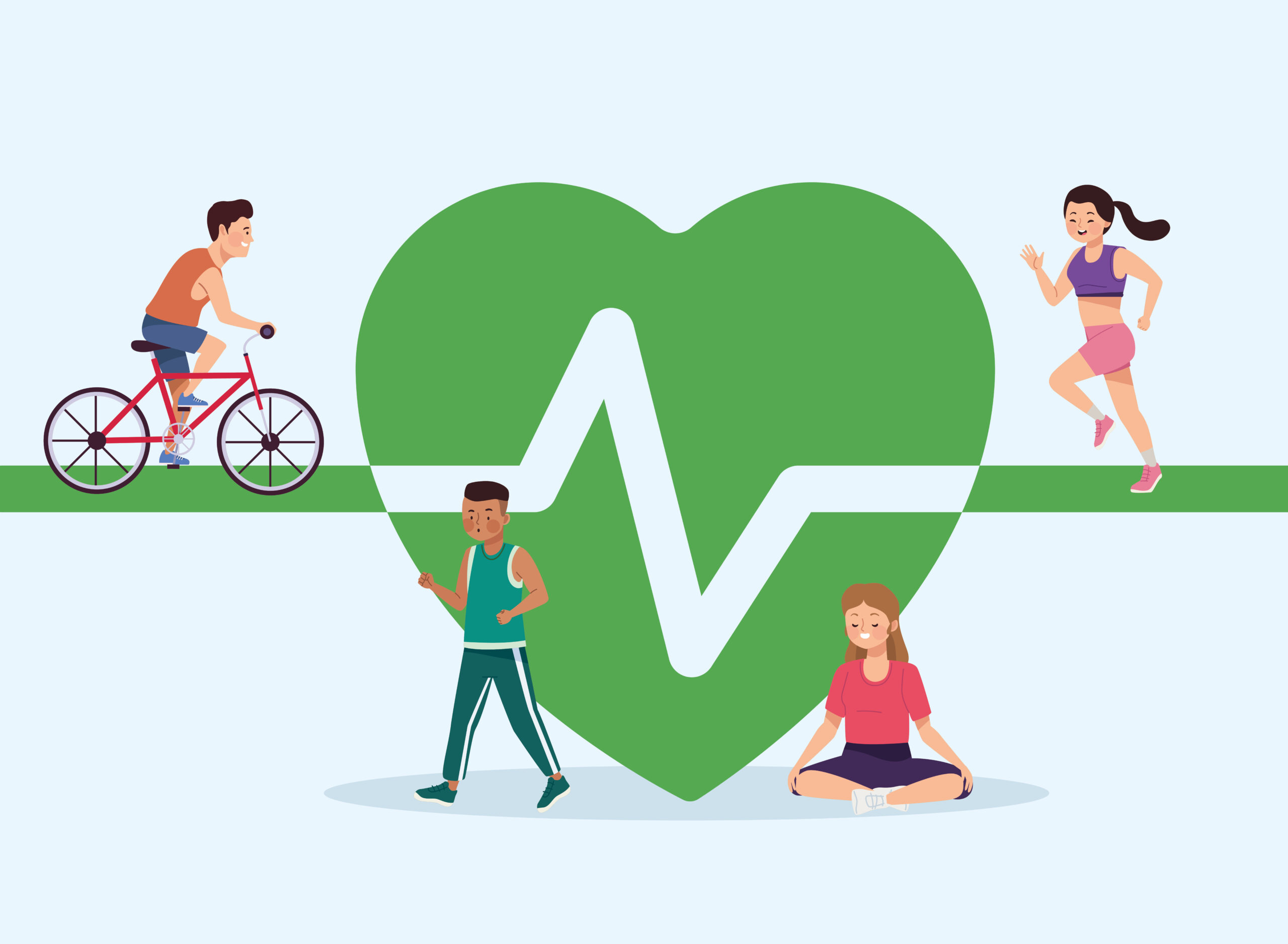

Incorporating cardiovascular exercise into your daily routine is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being, especially as you age. Engaging in regular physical activity can offer a myriad of benefits, from improving heart health to boosting fitness levels.

Benefits of Cardiovascular Exercises
Cardiovascular exercise is highly beneficial for Adults, promoting heart health and overall well-being. Regular activities can strengthen the heart, improve circulation, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Cardiovascular exercise also helps maintain a healthy weight, boosts energy levels, and promotes a positive mood. Adults should start with low-intensity exercises and gradually increase duration and intensity. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional and listen to your body, pacing yourself and allowing for proper rest and recovery.


Heart Health and Aging: The Role of Cardiovascular Exercise
Maintaining heart health is crucial as we age, and cardiovascular exercise plays a vital role in achieving this. Engaging in activities like brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or dancing helps strengthen the heart, improve blood flow, and lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Regular cardiovascular exercise also promotes healthy cholesterol levels, reduces blood pressure, and enhances overall cardiovascular function, ensuring a healthier and more active aging process.
Also read, Back Pain: 3 Best Exercises For Relief


Safe and Effective Cardiovascular Workouts for Adults
For Adults, safe and effective cardiovascular workouts are essential for maintaining overall health. Some options include
- brisk walking
- swimming
- cycling
- jogging
- low-impact aerobics
- chair exercises
- dancing.
These exercises improve heart health, strengthen muscles, and enhance overall fitness. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise program, listen to your body, and gradually increase intensity. Safety should always be a top priority for Adults engaging in cardiovascular workouts.

How to Choose the Right Cardiovascular Exercise for You?
There are many different types of cardiovascular exercise, so it is important to choose one that you enjoy and that fits into your lifestyle. Here are a few things to consider when choosing a cardiovascular exercise:
- Your fitness level: If you are new to exercise, you will want to start with a low-intensity activity. As you get fitter, you can gradually increase the intensity of your workouts.
- Your interests: If you enjoy being outdoors, you might want to choose an activity like walking, running, or biking. If you prefer to work out indoors, you might want to try swimming, dancing, or yoga.
- Your schedule: If you are short on time, you might want to choose an activity that you can do at home, such as walking or yoga.
How to Start a Cardiovascular Exercise Program?
If you are new to exercise, it is important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. Here are some tips for starting a cardiovascular exercise program:
- Start with 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise 3-4 times per week.
- Gradually increase the intensity or duration of your workouts each week.
- Listen to your body and take breaks when you need them.
- Talk to your doctor before starting any new exercise program.
Warm Up and Cool Down
It’s important to warm up before you start any cardiovascular exercise and cool down afterward. Warming up helps to prepare your body for exercise and reduce your risk of injury. Cooling down helps your body to recover from exercise and prevents muscle soreness.

Conclusion
Engaging in cardiovascular exercise is vital for adults to maintain optimal health, fitness, and overall well-being. By incorporating regular workouts into their routines, adults can experience the numerous benefits that cardiovascular exercise offers. Whether it’s brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, finding enjoyable and safe activities will help individuals stay active, age gracefully, and enjoy a healthier life.

Disclaimer: This blog provides general information and encourages seeking medical care for specific conditions. It is important to note that this information is not a substitute for medical advice, and we cannot be held responsible for any consequences.
Dr Owais Rafiq
Subscribe to Dr Owais YouTube channel
For parenting advice, child health, symptoms, causes and treatment of illness in children.