Parental Stress (Healthy Minds Adults)
- Dr Owais Rafiq
- September 28, 2023
- 8:52 pm

Introduction

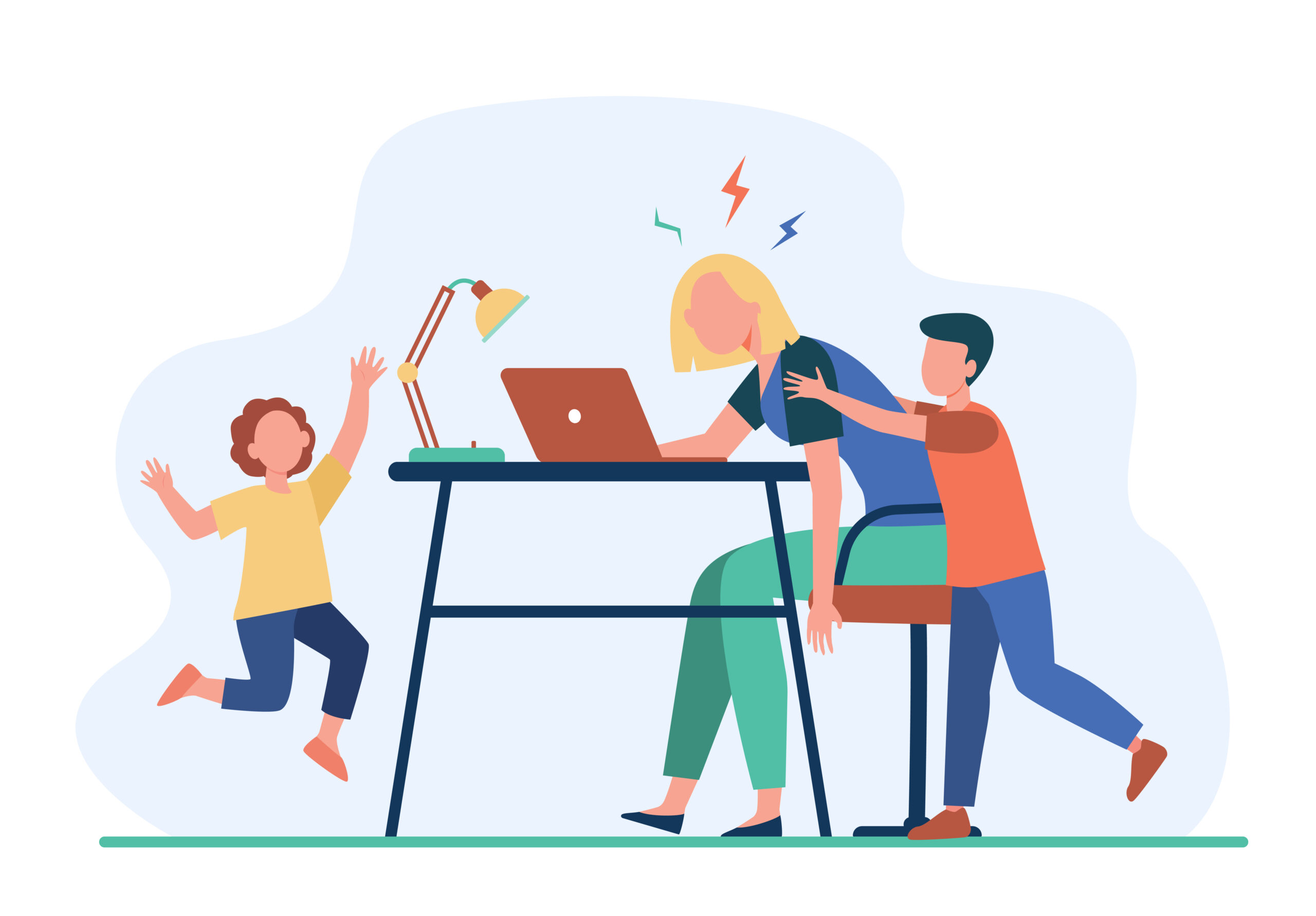
Parenting brings joy, but it also comes with challenges. Parental stress is the strain parents feel when they face the demands of raising children. It can affect their mental and physical health, as well as their children’s well-being. In this blog, we’ll explore the causes of parenting stress, and its effects, and share practical strategies to cope with it.
Understanding Parental Stress:
Parental stress refers to the emotional and physical strain experienced by parents in response to the demands and pressures of parenting. It can arise from various sources, such as financial worries, lack of support, time constraints, and concerns about child development. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of parenting stress is crucial for effective management. These may include:
- Irritability
- Difficulty sleeping
- Lack of concentration
- Increased use of substances like alcohol or tobacco
- Loss of enjoyment
- Constant feeling of tension
Causes of Parental Stress:
- High Expectations: Feeling pressure to be a “perfect” parent can lead to stress and self-doubt.
- Lack of Support: Not having enough help or feeling isolated can make stress worse.
- Time and Money Constraints: Balancing work, chores, and parenting can be tough, especially when time and money are limited.
- Relationship Strains: Disagreements with a partner or co-parent can add stress.
- External Pressures: Societal expectations and cultural norms, as well as pressure from family, can contribute to stress.

The Impact of Parental Stress on Parents and Children:
Parental stress also affects busy parents and their children. Here are some impacts to consider,
Parental Health:
Chronic stress can cause physical health problems like high blood pressure, sleep issues, and a weakened immune system.
Mental Well-being:
Stress can lead to anxiety, depression, irritability, and less happiness in life.

High levels of parental stress not only affect parents’ well-being but can also have a significant impact on children. Parents experiencing chronic stress may find it challenging to provide consistent care and emotional support to their children. This can lead to:
- Behavioral issues
- Reduced parent-child bonding
- Negative Effects on Children’s Social and Emotional Development
- Reduced academic performance.

Breaking the cycle of stress is essential for the overall well-being of both parents and children.
Coping Strategies for Parenting Stress:
- Take Care of Yourself: Prioritize self-care by doing activities that help you relax and feel good, like exercise, hobbies, and spending time with friends.
- Seek Support: Build a network of support by reaching out to family, friends, and parenting groups. Share your experiences and get guidance.
- Effective Communication: Talk openly and honestly with your partner or co-parent. Address conflicts together and find solutions.
- Manage Time: Create a realistic schedule that balances work, household tasks, and quality time with your children. Ask for help when needed.
- Set Realistic Expectations: Remember that perfection isn’t possible. Focus on progress instead of trying to be a perfect parent.
- Seek Professional Help: If parental stress becomes too much or starts affecting your daily life, consider seeing a therapist or counselor who specializes in parenting stress.

Disclaimer: This blog provides general information and encourages seeking medical care for specific conditions. It is important to note that this information is not a substitute for medical advice, and we cannot be held responsible for any consequences.
Dr Owais Rafiq
Subscribe to Dr Owais YouTube channel
For parenting advice, child health, symptoms, causes and treatment of illness in children.