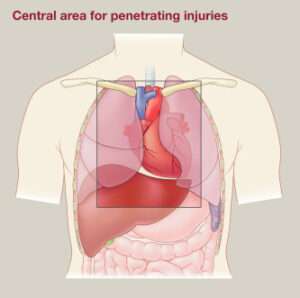
Penetrating Injuries Chest
- Dr Maryum Sohail
- February 15, 2024
- 10:48 pm

Penetrating chest injuries can be perilous and require prompt clinical consideration. These injuries are achieved by objects penetrating the chest pit, provoking anticipated mischief in principal organs like the heart, lungs, and huge veins.
Reasons for Penetrating Chest Injuries:
Firearms: Shot injuries are a huge reason for penetrating chest injuries in youngsters, frequently coming about because of mishaps, savagery, or carelessness.
- Stab wounds: Sharp objects such as knives, scissors, or broken glass can puncture the chest wall, causing severe damage.
- Impalements: Accidents involving objects like poles, spears, or metal rods can cause penetrating injuries to the chest.
Symptoms of Penetrating Chest Injuries:
- Difficulty breathing: Due to potential damage to the lungs or airways, children may experience shortness of breath or respiratory distress.
- Chest pain: Sharp and intense pain in the chest, worsened with breathing or movement, is a common symptom.
- Rapid heartbeat: Damage to the heart or major blood vessels can lead to an increased heart rate.
- Hypotension: Severe bleeding may result in low blood pressure, leading to shock.
After Penetrating Chest Injuries, A Child May Experience:
- Physical effects like wounds, bleeding, and potential damage to organs.
- Respiratory complications and difficulty breathing if the chest is injured.
- Neurological impairment, pain, and discomfort.
- Psychological effects, such as emotional trauma and behavioral changes.
- Risk of infection, sepsis, and long-term complications.
- Possible scarring, rehabilitation, and long-term medical treatment.
Also, Check: penetrating injuries abdomen
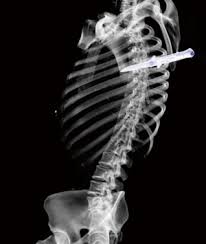
Immediate Actions:
If you suspect a kid has supported penetrating chest injuries, follow these means while hanging tight for clinical assistance:
- Call emergency services (911 or local emergency number) immediately.
- Loosen tight clothing around the chest.
- Keep the child in an upright or slightly forward-leaning position to ease breathing.
- Offer small sips of clear fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Wait until the child feels better before offering food if experiencing nausea or vomiting.
- Keep an eye on the child’s heart and breathing rate.
Penetrating Chest Injuries Treatment:
- Upon arrival at the hospital, the medical team will conduct a thorough evaluation, including physical examination, imaging scans, and diagnostic tests.
- Surgery is often required to remove the foreign object, repair damaged tissues, and control bleeding.
- In severe cases, emergency thoracotomy is needed, involving opening the chest cavity to access and address life-threatening injuries to the heart, lungs, or major blood vessels.
Postoperative Consideration and Recovery:
After the medical procedure, the youngster will be firmly observed in the emergency unit). During the recovery phase, pain management and infection prevention are essential.
Care at Home After Surgery:
- Follow wound care instructions provided by your doctor.
- Give prescribed pain medications and antibiotics as directed.
- Ensure the child rests and avoids strenuous activities.
- Offer a nutritious diet and keep the child hydrated.
- Practice good hand hygiene and maintain a clean home environment.
- Follow isolation guidelines if necessary.
Regaining Lung Function:
- Encourage deep breathing exercises.
- Teach effective coughing techniques.
- Encourage early mobility.
Physical therapy may be recommended to aid in lung function and overall healing.
Long-term Outlook:
- The prognosis for children with penetrating chest injuries depends on the extent of damage, promptness of medical intervention, and overall health.
- Some children may experience physical and emotional trauma, requiring counselling and support during their recovery.
Conclusion:
Penetrating chest injuries are serious medical emergencies that call for immediate treatment. Figuring out the causes, side effects, and treatment choices can assist with saving lives and work on long-haul results for impacted youngsters. Continuously focus on well-being and go to precautionary lengths to stay away from such occurrences, and in the event of a crisis, look for clinical help immediately.
Dr Maryum Sohail
Subscribe to Dr Owais YouTube channel
For parenting advice, child health, symptoms, causes and treatment of illness in children.